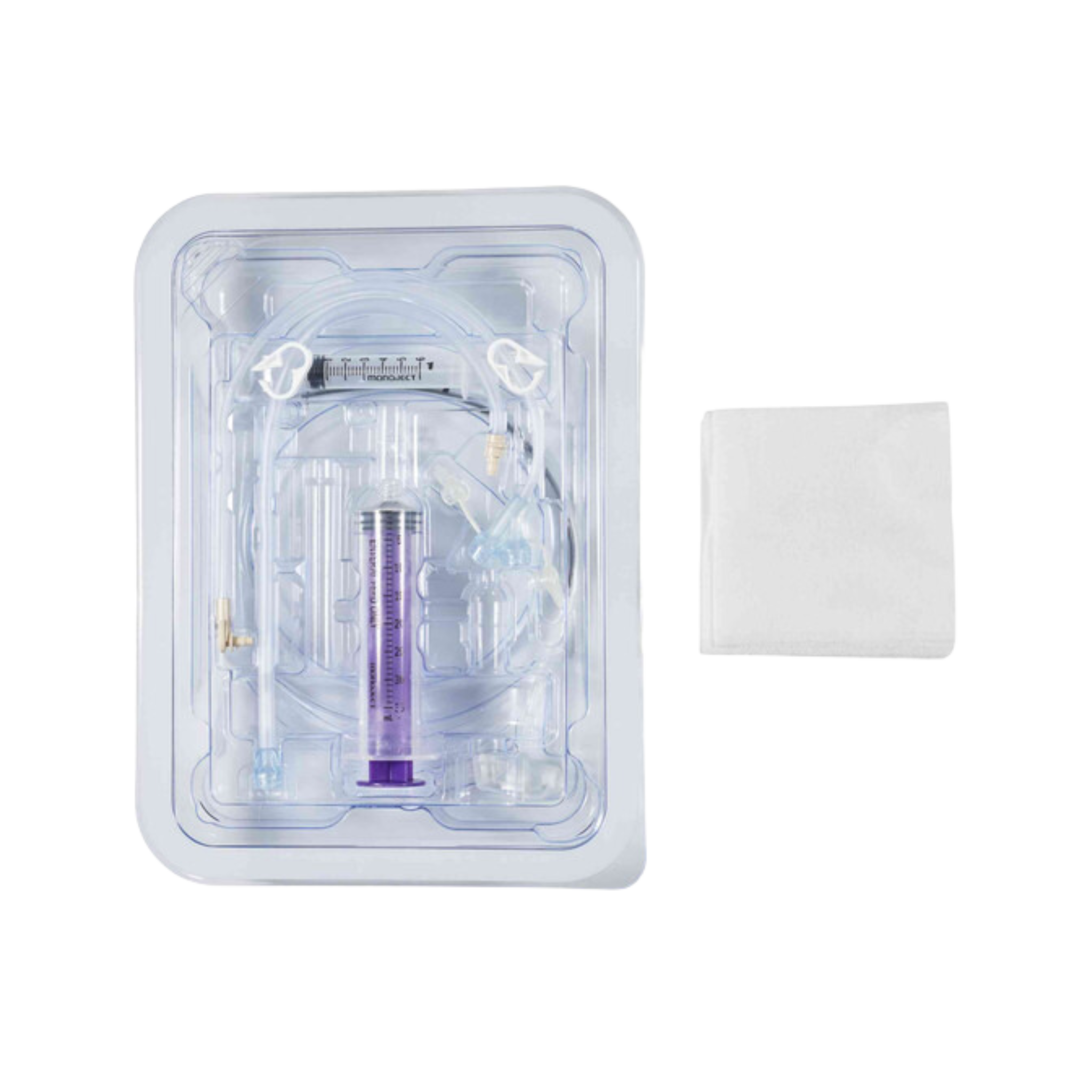
Jejunal Feeding Tube: Reliable Solutions for Enteral Nutrition
Explore top-quality low-profile jejunal feeding tubes including gastric and mic-key variants for safe, long-term nutrition support.
Summary
Jejunal feeding tubes provide critical support for patients requiring long-term enteral nutrition due to impaired gastrointestinal function. This comprehensive guide explains what jejunal feeding tubes are, who they’re for, their types—including mic-key, gastric, and nasojejunal variations—and how to choose the right one. We also introduce high-quality Avanos low-profile feeding tubes, available in multiple French sizes, ideal for clinical and home care settings.
Understanding Jejunal Feeding Tubes
A jejunal feeding tube is a medical device inserted into the jejunum (a part of the small intestine) for direct nutrient delivery. This method is typically used when oral intake is not possible or the stomach cannot process food efficiently. These tubes ensure patients receive essential calories, fluids, and medications safely and effectively.
Common conditions requiring jejunal tube feeding include:
- Severe gastroparesis
- Neurological disorders (e.g., stroke, ALS)
- Pancreatitis
- Upper GI obstructions
- Post-surgical complications
Unlike nasogastric tubes, which pass through the nose, jejunal tubes are often inserted percutaneously or surgically for longer-term use, often under fluoroscopy or endoscopy guidance.
Benefits of Low-Profile Jejunal Tubes
Low-profile feeding tubes, such as the Avanos Mic-Key range, offer significant advantages in long-term enteral care:
- Discreet and Comfortable: These button-style devices sit flush with the skin, making them ideal for daily wear.
- Secure and Safe: Locking mechanisms reduce accidental dislodgment.
- Enfit Compatibility: Enhances patient safety with unique, misconnection-resistant connectors.
- Multiple Size Options: Including 14Fr, 18Fr, and 22Fr variants to suit different age groups and needs.
Procedure, Care, and Maintenance
Proper insertion, care, and monitoring of a jejunal feeding tube are essential to avoid complications such as dislodgement, infection, or clogging.
Insertion Procedure:
- Typically guided by imaging (fluoroscopy or endoscopy)
- Administered under sedation or general anaesthesia
- Placement confirmed via X-ray
Daily Care Includes:
- Flushing the tube regularly (before and after feeds and medications)
- Cleaning the stoma site
- Monitoring for leaks, redness, or irritation
Replacing and Managing Buttons:
Low-profile tubes include button extensions that can wear out over time and need replacement.
Patient Support Tips:
- Use a gentle feeding schedule
- Sit upright for 30–60 minutes post-feeding
- Rotate feeding extension sets regularly
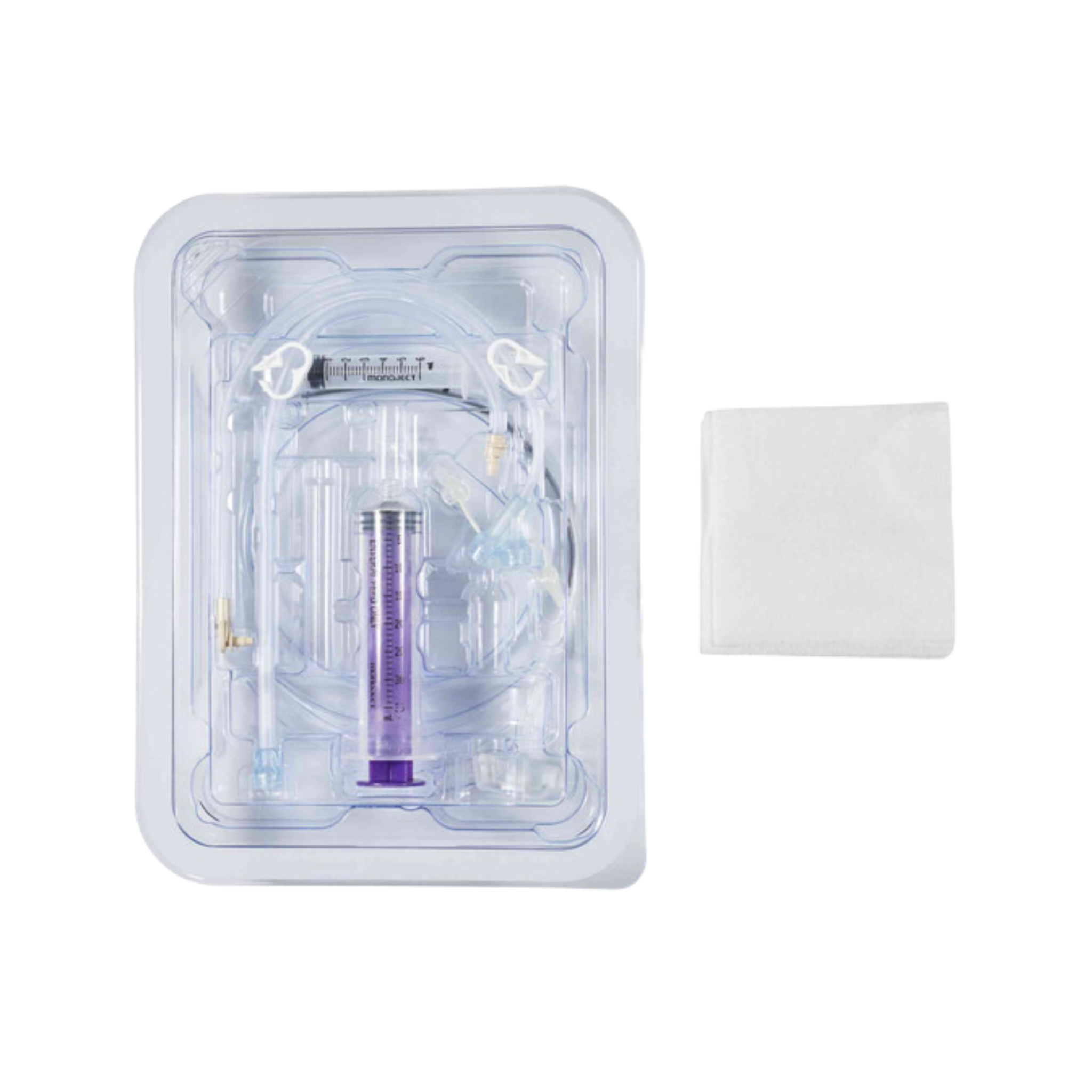
For visual learners, reviewing a jejunal feeding tube picture can help familiarise with setup and expectations.
Featured Products

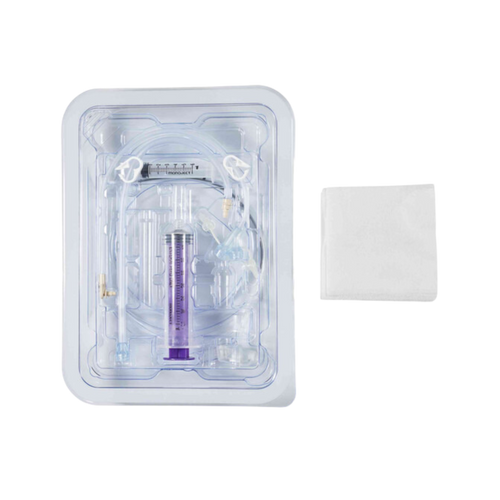
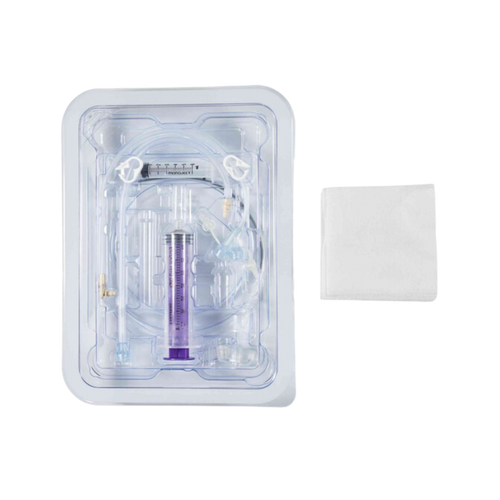
Types of Jejunal Feeding Tubes
Choosing the right jejunal feeding tube depends on clinical needs, duration of therapy, and patient comfort. Below are the most common types:
-
1. Mic-Jejunal Feeding Tubes
- Low-profile, button-style tubes
- Discreet and ideal for active patients
- Popular models include the Avanos Mic-Key Jejunal Tube Enfit Extension Sets
-
2. Gastric-Jejunal Tubes (GJ Tubes)
- Serve dual purposes: one port to the stomach, another to the jejunum
- Useful for patients with both reflux and delayed gastric emptying
-
3. Nasal Jejunal Feeding Tubes
- Inserted via the nasal passage and guided into the jejunum
- Often used temporarily in hospital settings
-
4. Transesophageal Jejunal Tubes
- Rarely used but applicable in complex cases
- Inserted through an esophageal stoma
Safety and Clinical Considerations
Jejunal tube feeding is generally safe, but certain precautions should be taken:
- Risk of aspiration is lower than gastric tubes
- Risk of bowel perforation exists during insertion—hence the need for skilled operators
- Not all patients are suitable candidates—individual evaluation is essential
Professional Recommendations:
According to the Australian Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (AuSPEN), jejunal feeding is preferred over gastric feeding in patients at high risk for aspiration or with severe gastric motility issues.
Conclusion
Jejunal feeding tubes play a crucial role in enteral nutrition support for patients with complex gastrointestinal needs. Whether you're seeking a mic-key low-profile solution or a gastric-jejunal tube, understanding the right type, care routine, and product specifications ensures both comfort and clinical success.
If you're a clinician, caregiver, or hospital procurement specialist, explore our premium Avanos jejunal tube range, available in multiple sizes with secure, Enfit-compatible designs.
Support long-term nutrition safely and confidently.
Browse our Jejunal Feeding Tube range today or contact our support team for clinical assistance and product recommendations.
📞 Call 1300 615 193 or order online at our website.
Jejungal feeding tube solutions support safe, long-term enteral nutrition for patients who cannot tolerate gastric feeding. This collection features low-profile jejunal and gastric-jejunal feeding tubes with ENFit connectors, designed for clinical reliability, patient comfort and home-care use across Australia.
Items included in this collection:
• Low-profile jejunal feeding tubes (Mic-Key style)
• Gastric-jejunal (GJ) feeding tubes for dual access
• ENFit-compatible extension sets for safe feeding
• Multiple French sizes (14Fr, 18Fr, 22Fr and more)
• Replacement buttons and feeding accessories


Recently viewed
FAQs
It delivers nutrition directly into the jejunum for patients who cannot tolerate stomach feeding or have high aspiration risk.
Jejunal tubes feed only into the small intestine, while GJ tubes allow feeding into the jejunum and drainage from the stomach.
Yes. ENFit connectors reduce misconnection risk and are the current safety standard in Australia for enteral feeding.
Yes. Low-profile jejunal feeding tubes are designed for long-term home use with proper clinical training and routine care.